Knowledge
Knowledge
Overview of Various Product Production Processes
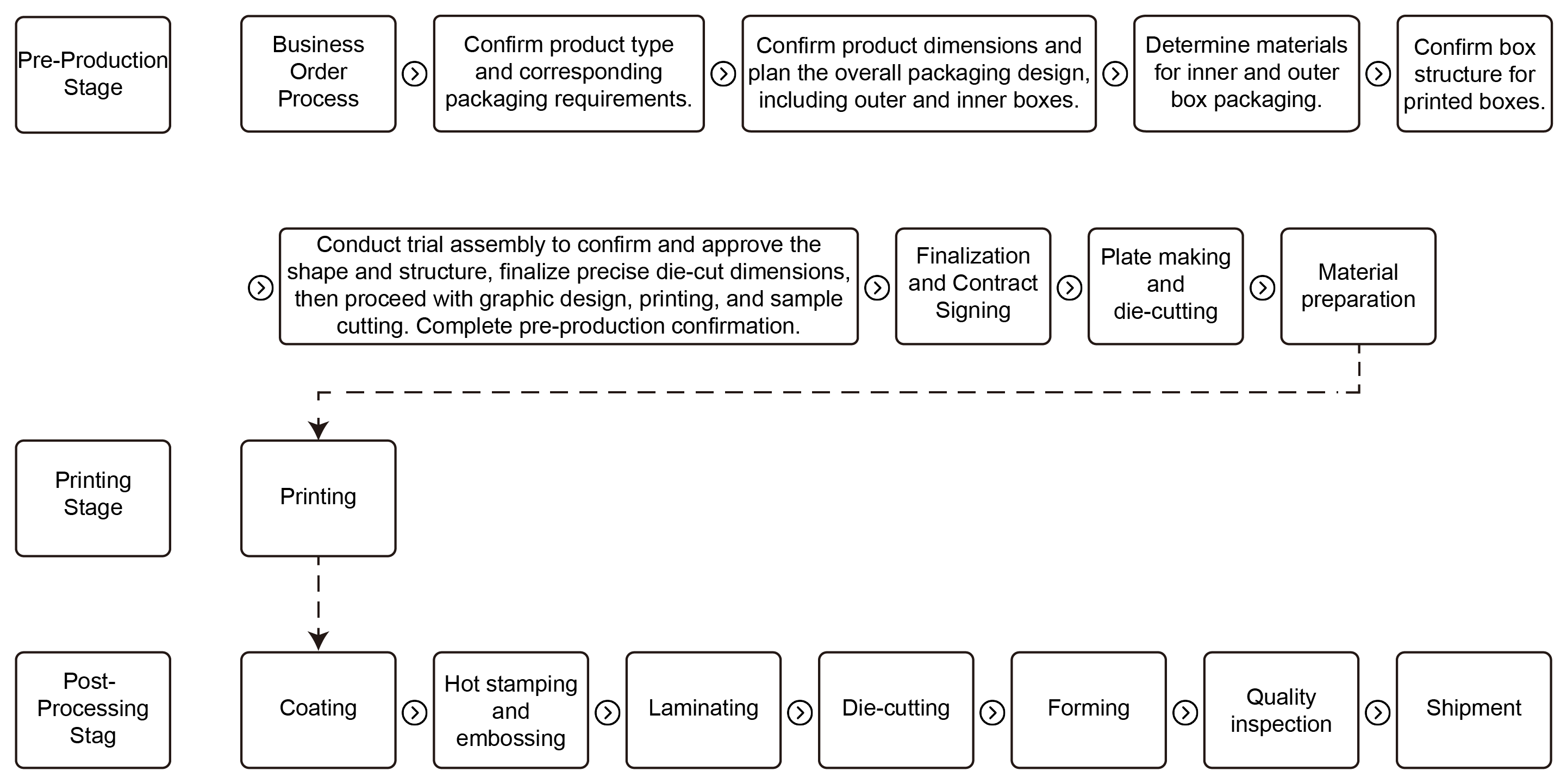
1 Product Production Process
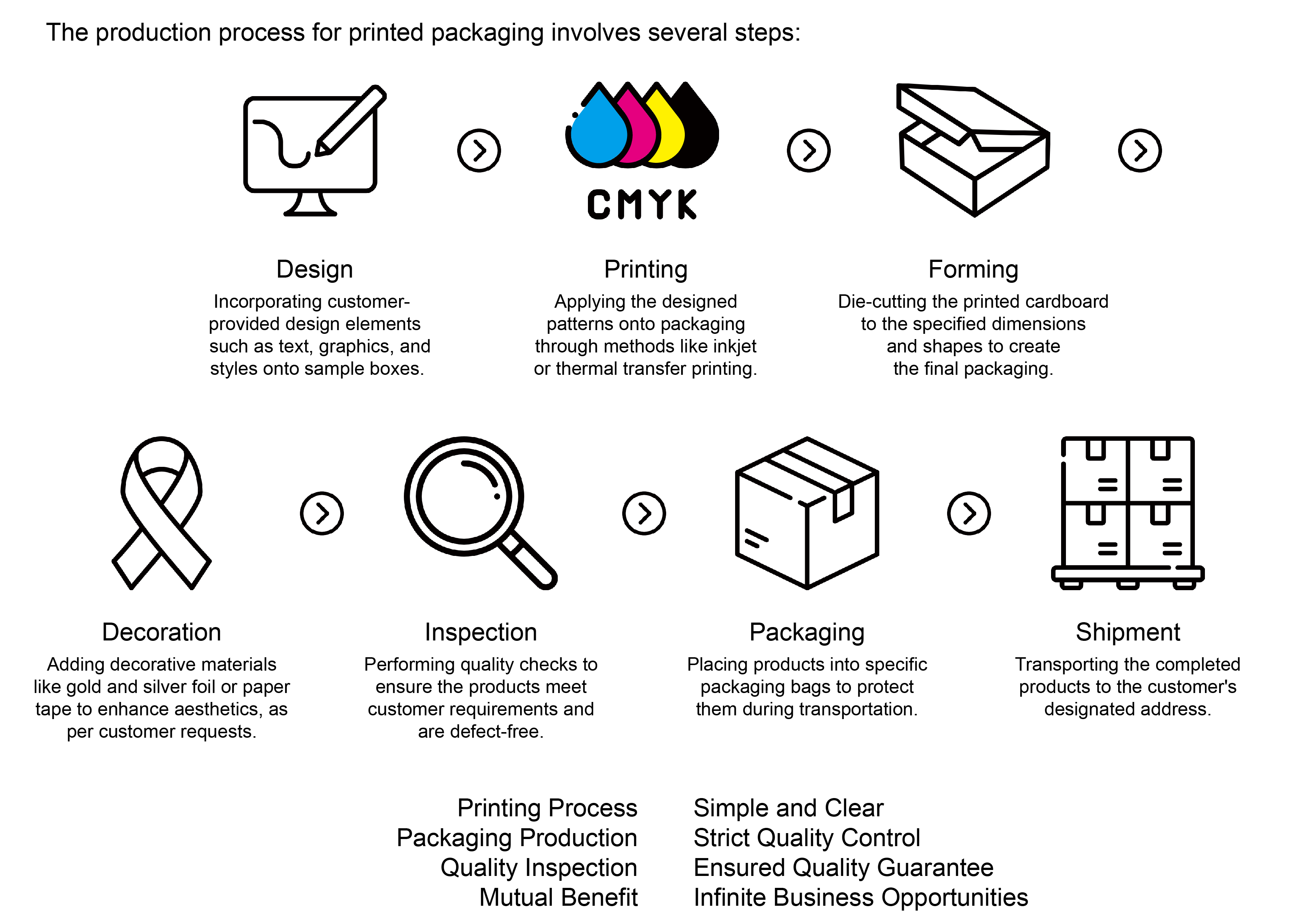
2 Introduction to Common Cardstock
There is an inseparable relationship between printing and paper types. Different printing projects require different types of paper to achieve the best results. Paper characteristics such as thickness, texture, quality, and surface treatment all influence the final quality and appearance of printed materials. For example, glossy paper is suitable for color printing, while rough-textured paper can create special effects. Additionally, the absorbency, load-bearing capacity, and durability of the paper will affect its performance during the printing process.
Therefore, when selecting the type of paper, it's crucial to consider the needs and purpose of the printing project. Below are introductions to several common types of paper.
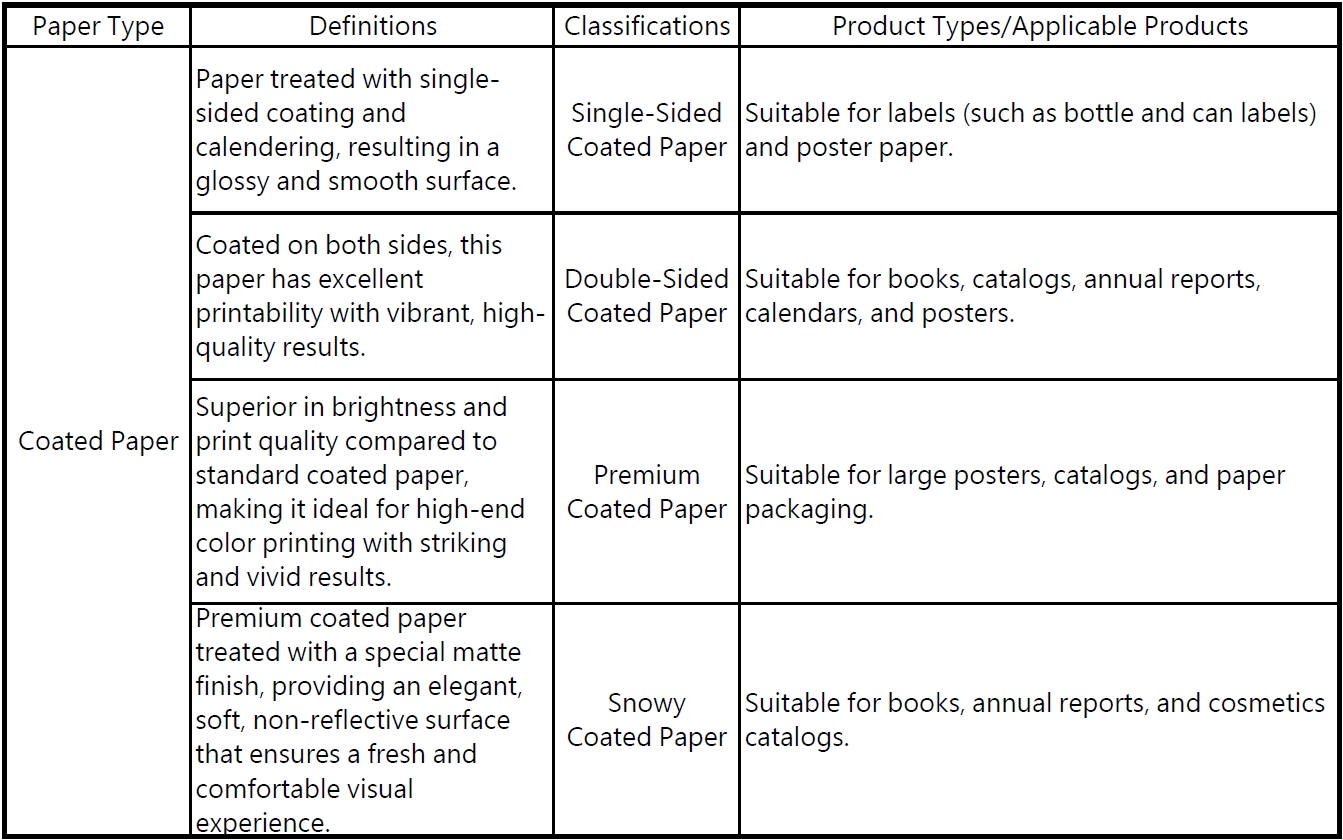
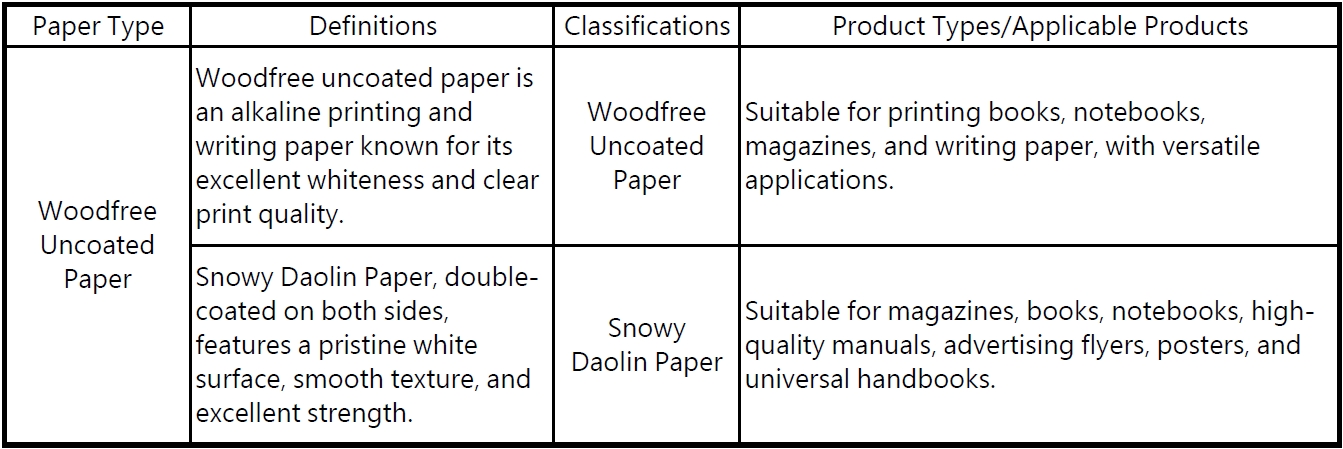
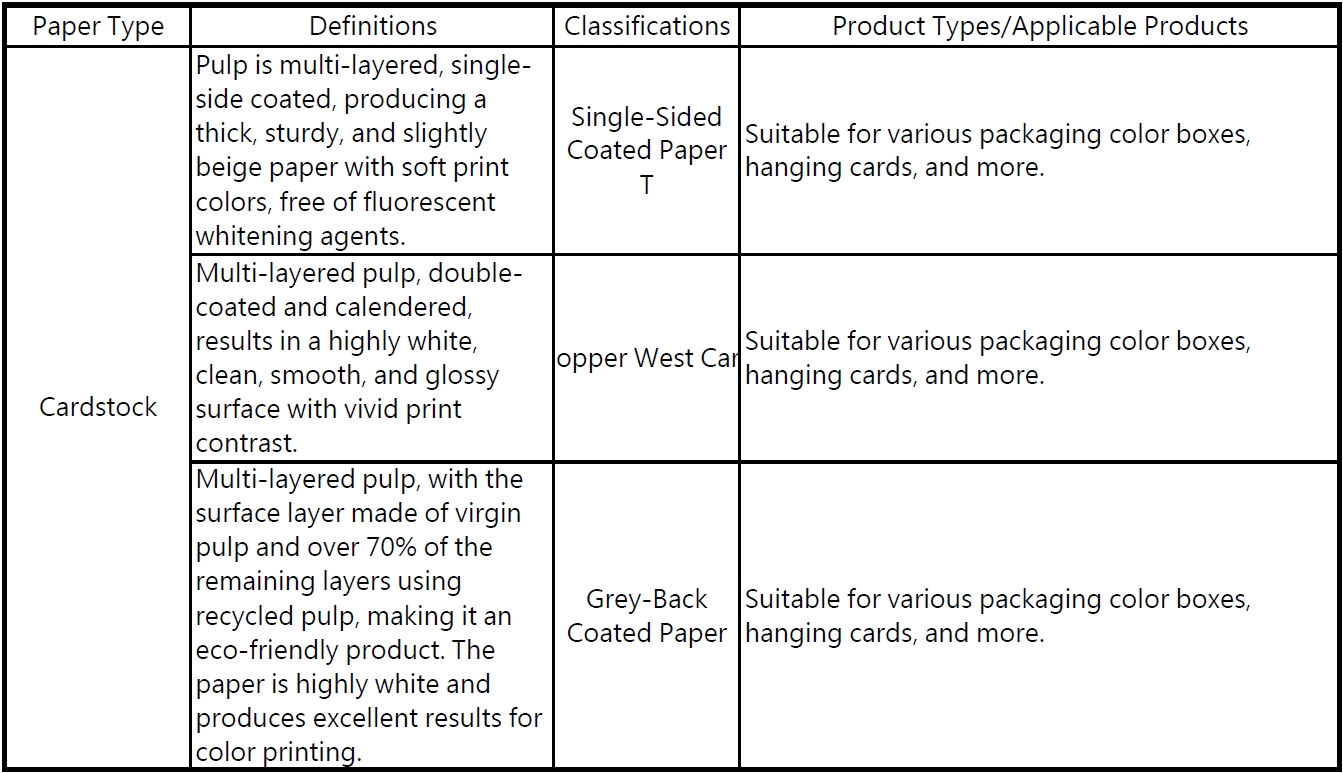
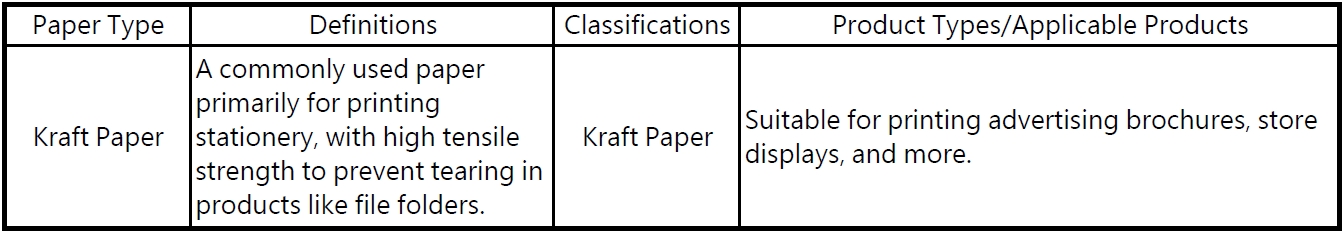
Other commonly used papers include:
-
Jinsha White Card
-
Matte Silver and Glossy Silver, Aluminum Foil Card
-
Single-Sided Laminated Paper
-
Pearl Card
-
White Pearl Card
-
Shimmer Pearl Card
-
Finnish Card
-
Federal Card
-
Lilai Card
-
Keli Card
These options can create different visual effects, and consumers can choose based on their main uses.
Each type of commonly used paper has unique properties and applications, suitable for various printing needs. When printing, it is recommended to select the most appropriate type of paper based on the product's characteristics and intended use to achieve the best printing results.
3 Introduction to Common Corrugated Cardboard
Corrugated cardboard boxes are extremely popular packaging materials, widely used across various industries, and are the preferred choice for most product packaging. Here are their key features:
1. Strong Structure: Made from a series of vertically and horizontally arranged paperboards, corrugated boxes are crafted from multiple layers of paperboard. They provide robust structural support without adding weight, offering excellent tensile strength. They are suitable for carrying heavy items, making them an ideal choice for transporting heavy products.
2. Protective: Corrugated boxes effectively protect products by reducing the risk of damage, including contamination and impacts, ensuring the integrity of the product during transportation and storage.
3. Eco-Friendly: The manufacturing process of corrugated boxes is closely linked to environmental protection. From the selection of raw materials to the control of the manufacturing process and the recycling and reuse of products, it reflects a concern for and responsibility towards the environment.
4. Product Identification: The surface of corrugated boxes can be printed with advertisements and brand information, helping consumers quickly identify the packaging contents, thus enhancing product visibility.
5. Brand Image: Printing advertisements and brand information on the surface of corrugated boxes helps enhance brand image and product exposure.
6. Cost-Effective: Compared to other packaging materials, corrugated boxes are cost-effective, offering an economical packaging solution.
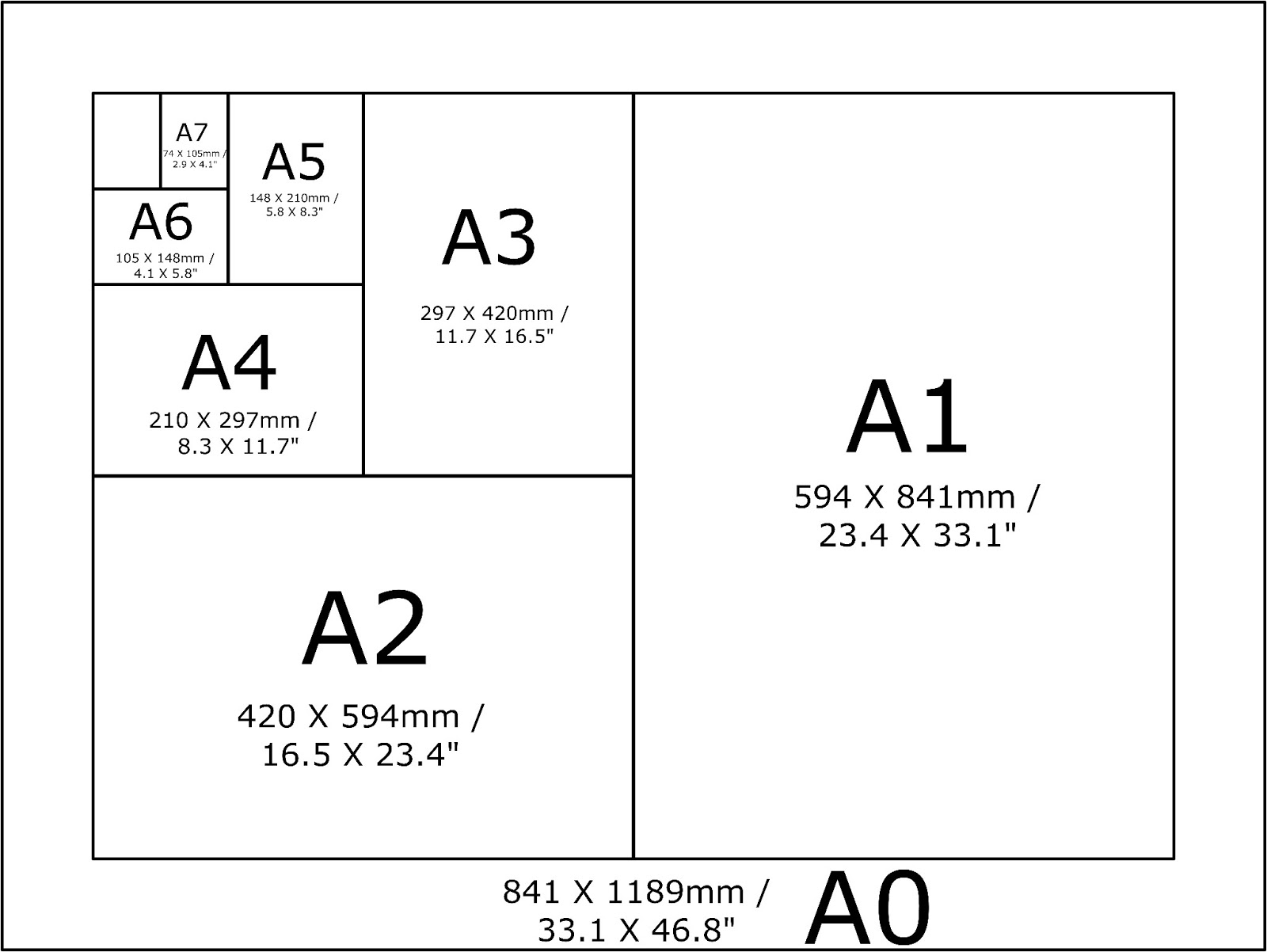
4 Paper Size Dimensions
Paper size dimensions are terms used to measure paper sizes, such as A4 paper, which is 210mm x 297mm. The paper size dimensions are represented as A4.
Here are the sizes:
-
A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5
-
B0, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5
-
C0, C1, C2, C3, C4, C5
A0 is the largest, measuring 841mm x 1189mm, and A5 is the smallest, measuring 148mm x 210mm.
The relationships between the sizes are as follows:
-
A0 is twice the size of A1,
-
A1 is twice the size of A2,
-
A2 is twice the size of A3,
-
A3 is twice the size of A4,
-
A4 is twice the size of A5,
-
B0 is twice the size of B1,
-
B1 is twice the size of B2,
-
B2 is twice the size of B3,
-
B3 is twice the size of B4,
-
B4 is twice the size of B5,
-
C0 is twice the size of C1,
-
C1 is twice the size of C2,
-
C2 is twice the size of C3,
-
C3 is twice the size of C4,
-
C4 is twice the size of C5.
Paper size dimensions can be used in various printing applications, such as books, newspapers, advertisements, and more. They provide optimal quality during printing while saving paper and costs.
5 Overview of Printing Colors
Printing colors play a crucial role in the printing industry, directly influencing the quality and visual impact of printed materials. Here is a brief explanation of different forms and principles of printing colors:
1. CMYK Four-Color Printing:
-
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black.
-
This printing method uses the subtractive color process, combining these four primary color inks to produce other colors.
-
The CMYK color model is suitable for printed materials because it can simulate a wide range of colors.
2. Spot Colors:
-
Spot colors refer to additional colors beyond CMYK, typically used for specific needs.
-
Common spot color systems include PANTONE, DIC, etc.
-
PANTONE colors are the most widely used in the market, not because other color systems are inferior, but because most ink supplies are based on PANTONE standards.
-
Some PANTONE colors can be replaced by CMYK four-color printing, but most still require the use of spot colors.
3. Color Systems:
-
Depending on customer requirements, different color systems can be used in printing, such as the Pantone color library.
-
The principle of spot colors differs from CMYK; they use specially formulated inks to achieve specific color effects.
The selection and application of printing colors are crucial to the final effect of printed materials. Based on customer needs, different color systems can be chosen to achieve the desired visual effect. If you have any further questions, feel free to ask!
6 Introduction to UV Printing
1. What is UV Printing?
-
UV printing is a digital printing technology that uses ultraviolet (UV) light to cure or dry the ink on a medium, creating the printed effect.
-
UV inks have superior curing strength compared to wet printing, resulting in more durable prints.
-
This method produces high-quality prints with vibrant and delicate colors and has excellent anti-aging properties.
2. Application Range:
-
UV printing is suitable for various media, including metal, plastic, and paper.
-
It is particularly effective for printing fine patterns, producing more delicate effects compared to wet printing.
-
The use of UV light for curing inks eliminates wet printing issues, enhancing the durability of the prints.
3. Advantages:
-
Low energy consumption, environmentally friendly, and efficient.
-
Lower costs, saving printing time and improving efficiency.
-
Multiple steps are completed in a single process, reducing time and costs.
4. Broad Application:
-
UV printing is used in industries such as advertising, electronics, paper products, and books.
-
It meets the printing needs of various industries, enhancing efficiency.
Feel free to ask if you have any more questions or need further details!
7 Order Processing Workflow
生產流程
Client Requirements
Client Request for Printing
Front-End Discussion
Coordination of Requirement Details
Related Quotation
Order Acceptance
Template Setup, Proofing, Procurement
Plate Making
Plate Production
Custom Molds
Printing
Inspection and Color Matching
Post-Printing Processing
Varnishing (Glossy, Matte, Satin)
Additional Processing
Hot Stamping, Embossing
Paper Laminating
Corrugated Cardboard, Cardstock
Cutting
Calibration, Cutting
Forming
Box Gluing, Nailing, Stacking
Final Quality Inspection
Quality Inspection, Counting, Labeling
Shipping
Transport Finished Products to Destination
8 FSC® Environmental Certification
FSC® (Forest Stewardship Council) is a global non-profit organization dedicated to promoting responsible forest management. It establishes standards to ensure the sustainability of forest resources and awards FSC® certification to forest managers and products that meet these standards.
FSC® Industry Knowledge:
1. Certification Standards:
-
Forest Management Certification: Ensures that forest operations meet standards of environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic sustainability.
-
Product Certification: Certifies the supply chain of products involving wood and paper, ensuring these products originate from certified forests and comply with FSC® requirements.
2. FSC Labels:
-
The label indicates that the product comes from forests that meet FSC® standards, helping consumers identify and select sustainably sourced products.
3. Three Main Categories:
-
FSC® 100%: All the wood in the product comes from FSC® certified forests.
-
FSC® Mix: The product contains a mix of FSC® certified and non-certified materials but must meet certain ratios and standards.
-
FSC® Recycled: The product is made from recycled materials and meets FSC® recycling standards.
4. Environmental and Social Standards:
-
Environmental Protection: Ensures forest operations do not excessively harm ecosystems and promotes the protection of biodiversity.
-
Social Responsibility: Safeguards the rights of local communities, promotes fair labor conditions, and collaborates with indigenous peoples.
5. Global Impact:
-
FSC® operates in multiple countries and regions globally, with its standards widely recognized and promoted in many international markets.
FSC®'s goal is to promote sustainable forest management, protect the environment, and support social and economic development.
9 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory
ISO 14064-1 is an international standard focused on the measurement, reporting, and verification of greenhouse gases (GHG). Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it aims to help organizations and businesses manage their greenhouse gas emissions while ensuring transparency and consistency.
ISO 14064-1 Industry Knowledge:
1. Scope of the Standard:
-
ISO 14064-1 focuses on the measurement and reporting of greenhouse gases, covering organizational-level emissions, including both direct and indirect emissions.
2. Greenhouse Gas Scopes:
-
Scope 1 (Direct Emissions): Emissions from sources owned or controlled by the organization, such as the combustion of fossil fuels.
-
Scope 2 (Indirect Emissions): Emissions from purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling.
-
Scope 3 (Other Indirect Emissions): Emissions throughout the entire value chain, including supplier emissions, transportation, and waste management.
3. Reporting Requirements:
-
Organizations need to establish a comprehensive GHG inventory and provide transparent, repeatable, and consistent reporting.
-
Reports must include emission quantities, data sources, calculation methods, as well as related assumptions and uncertainty assessments.
4. Verification and Validation:
-
ISO 14064-1 supports third-party verification of GHG reports to ensure their accuracy and reliability.
-
The verification process can be conducted by independent auditing bodies, helping organizations gain trust and certification.
5. Uses and Applications:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations meet governmental and environmental agency requirements.
-
Market Demand: Enhances transparency and credibility with investors, customers, and other stakeholders.
-
Corporate Strategy: Supports setting emission reduction targets and strategies, improving environmental performance.
6. Continuous Improvement:
-
The standard encourages organizations to continually improve their GHG management systems and periodically update and review reports.
ISO 14064-1 provides a framework to help organizations accurately measure and manage their greenhouse gas emissions, supporting global reduction efforts and promoting sustainable development.